<!-- 以下依赖也集成了 MyBatis -->
<!-- Spring 2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring 3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-spring-boot3-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>[!quote] MyBatis Plus MyBatis 偏向于定制化开发,MyBatis Plus 也不是用来替换 MyBatis 的,是在 MyBatis 的基础上提供的一套增强功能,而且只适合单表的 CRUD,对于多表还是需要手写 SQL 语句
常用注解
[!hint] MyBatis Plus 中的默认处理方式
- MP 默认会把实体类名的驼峰命名转下划线作为表名【
UserInfo 转为 user_info】- 实体类的变量名驼峰命名转下划线作为字段名
- 名为 id 的变量作为主键
加在实体类上
@TableName("表明")指定表名
@TableName("user")
public class User {……}@TableId指定主键value指定主键字段名typeIdType.AUTO表示数据库表的主键是自增长的IdType.INPUT表示数据库表的主键由程序员自己定义IdType.ASSIGN_ID表示数据库表的主键由雪花算法自动生成【默认】
public class UserEntity {
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long userId;
}@TableField指定其他字段名exist = false在映射数据库字段时,忽略这个属性
以下情况,一定要加 `@TableField`
- 由于 MP 的机制,如果实体类中的某个属性名是以
is开头的,那一定要指定@TableField,因为在反射处理时会去掉is - 实体类中的属性名是数据库的关键字【
比如】时order - 实体类中的属性名不是数据库中的字段
public class User {
@TableField("is_married")
private Boolean isMarried;
// 此处要加''
@TableField("'order'")
private Integer order;
// 该属性不是数据库字段
@TableField(exist = false)
private String address
}常用配置
[!hint] 大部分配置都是默认的,不用自己配,除非特殊需求要用到
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath:/mapper/*.xml # 指定Mapper XML文件的位置
type-aliases-package: com.yourpackage.domain # 指定所有实体类的所在包
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: AUTO # 全局的主键策略
insert-strategy: NOT_NULL # 插入策略,只插入非空字段
update-strategy: NOT_NULL # 更新策略
select-strategy: NOT_NULL # 查询策略
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)
banner: false # 是否显示MyBatis Plus启动横幅
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true # 是否开启自动驼峰命名规则
cache-enabled: false # 是否开启二级缓存
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.slf4j.Slf4jImpl # 打印操作的日志
jdbc-type-for-null: 'null' # 指定JDBC的null类型
settings:
use-generated-keys: true # 是否使用数据库自增主键
use-column-label: true # 使用列标签代替列名
log-execute-time: 100 # 执行慢的SQL阈值
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 打印SQL日志的实现类核心功能
简单 CRUD
- 配置 yml 文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security
username: root
password: ……- 定义实体类,并使用
@TableName指定表名
package com.example.Pojo;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
// 定义实体类对应的数据库中的表名
@TableName("user")
public class userPlus {
private Long userId; // 用户ID
private String userName; // 用户名
private String userPassword; // 用户密码
private Integer userAuthority; // 用户权限
}- 让 Mapper 继承
BaseMapper<实体类>
@Mapper
public interface UserMapperPlus extends BaseMapper<userPlus> {}[!quote]+
BaseMapper<T>BaseMapper<T>里面定义了常用的增删改查代码
- 增
insertSelective(T record)插入一条记录(选择字段,策略插入)- 删
deleteById(Serializable id)根据 ID 删除deleteByMap(@Param("et") T entity)根据 column 删除- 改
updateById(@Param("et") T record)根据 ID 修改- 查
selectById(Serializable id)根据 ID 查询selectBatchIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList)根据 ID 集合来批量查询selectByMap(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)查询(根据 column 查询)selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)总记录数selectCountByMap(@Param("ew") T entity)总记录数(根据 column 查询)selectMapsPage(@Param("current") int current, @Param("size") int size, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)根据 column 统计selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)根据 column 统计(不分页)selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)根据 column 统计(统计字段为 ID)selectObjsByPage(@Param("current") int current, @Param("size") int size, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)根据 column 统计(统计字段为 ID,不分页)selectObjsNotNull(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)根据 column 统计(统计字段为 ID,不分页)selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> example)根据 column 统计(统计字段为 ID,不分页)
- 测试
package com.example;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class MyBatisPlusTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapperPlus userMapperPlus;
@Test
public void testSelect() {
System.out.println(("----- selectAll method test ------"));
List<userPlus> userPluses = userMapperPlus.selectList(null);
userPluses.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
---
userPlus(userId=1, userName=kite, userPassword=$2a$10$NP/SbcLek9Q8hemltyG024K, userAuthority=1)
userPlus(userId=2, userName=nelson, userPassword=Fra, userAuthority=1)条件构造器
[!quote] 条件构造器 Wrapper
条件构造器 Wrapper 可以构造
WHERE条件,进行条件性地 RUD继承体系:
AbstractWrapper
QueryWrapper专门用于 RD 操作,可以添加各种查询条件UpdateWrapper用于 U 操作,可以添加更新条件和更新的字段值,可以在不创建实体对象的情况下,直接设置更新字段和条件LambdaQueryWrapperLambdaUpdateWrapper
[!hint] 推荐使用
LambdaQueryWrapper,LambdaUpdateWrapper
- 防止硬编码:字段名直接从实体类属性中引用,不需要自己指定
- 类型安全:在编译期间,就可以保证实体类中的属性的数据类型和传入的数据一致
java// Lambda条件查询 @Test public void testSelectLambdaWrapper() { LambdaQueryWrapper\<User> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper\<User>() // 使用方法引用获取字段名,防止硬编码 .select(User::getUserName, User::getUserPassword) .like(User::getUserPassword, "K"); userMapper.selectList(lambdaQueryWrapper).forEach(System.out::println); }
[!quote] 在 BaseMapper 中需要传入 Wrapper 参数的方法
- 增
update(修改后的实体类对象, Wrapper wrapper)实体类中未设置的参数,不更改- 查
selectList(Wrapper<T> example)查询列表,传入参数为 null,则是查询整个表
QueryWrapper
- 前半段
setEntityClass(字节码文件)设置字节码文件,用于 Db Kit
- 后半段
- 大小等
eq("数据库字段", 条件值)设置单个字段的相等条件nq()设置单个字段的不相等条件gt()设置单个字段的大于条件 【greater than】ge()设置单个字段的大于等于条件lt()设置单个字段的小于条件le()设置单个字段的小于等于条件
- 范围
between("数据库字段", 值1, 值2)设置单个字段的 BETWEEN 条件notBetween(……)in("字段", 集合)设置单个字段的 IN 条件【字段的值在给定的集合中】
- 模糊匹配
like()设置单个字段的 LIKE 条件notLike()likeLeft()设置单个字段的左模糊匹配条件
isNull("数据库字段")判断单个字段的 IS NULL
- 大小等
// 更新用户权限
@Test
public void testUpdateUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setUserAuthority(2);
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.eq("user_id", 1);
userMapper.update(user, queryWrapper);
}
---
将id为1的行,的authority修改为2// 条件查询
@Test
public void testSelectWrapper() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.select("user_name", "user_password")
.like("user_password", "K");
userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}
---
User(userId=null, userName=jaygee, userPassword=Korea, userAuthority=null)
User(userId=null, userName=Hoan, userPassword=Korea, userAuthority=null)UpdateWrapper
如果在 UPDATE 时,SET 的条件是动态的【例如,某个字段减 200,而不是说设置某个字段为固定的值】,那就需要使用 UpdateWrapper
// UpdateWrapper动态SET
@Test
public void testUpdateWrapper() {
UpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<User>()
.setSql("user_authority = user_authority - 1")
.eq("user_id", 1);
userMapper.update(null, updateWrapper);
}
---
将id为 1 的行,authority字段的值减 1动态 SQL
[!quote] 动态 SQL 动态 SQL 就是可以使用条件来动态地判断是否要加入某个
WHERE 条件
eq(条件, 字段, 值)
// 使用IService多个条件动态查询
@Test
public void testIServiceMultiConditionDynamicSelect(User user) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<User>()
// 如果user.getId()不为空,则拼接这个条件
.eq(user.getId() != null, User::getId, user.getId())
.eq(user.getName() != null, User::getName, user.getName())
.eq(user.getPassword() != null, User::getPassword, user.getPassword());
User userResult = userService.getOne(lambdaQueryWrapper);
System.out.println(userResult);
}IService 接口
[!hint] 有了
IService,我们就很少用到BaseMapper了,除非需要自定义 SQL,虽然不用,但是也要创建BaseMapper,因为IService的实现类的泛型需要BaseMapper
[!quote] IService 接口
由于,Controller需要调Service不能直接调Mapper,所以我们引入了IService和ServiceImpl<Mapper, Entity>IService接口相对于BaseMapper<>功能只多不少。IService 有批处理功能,可以提高性能java// UserService 实现 IService public interface UserService extends IService\<User> { …… }java// UserServiceImpl 继承 ServiceImpl,这样就可以获得 ServiceImpl 里所有的方法 @Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService { …… }
- 增
save-插入
- 删
remove-删除
- 改
update-
- 查
get-查询单行list-查询集合page分页查询
// 使用IService查询单个
@Test
public void testIServiceGetOne() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.eq("user_id", 1);
User user = userService.getOne(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(user);
}
---
User(id=1, name=kite, password=Japen, authority=4)批量处理
[!hint] 在需要处理大量数据时,批处理可以提高性能
- 不使用批处理:发送网络请求次数较多,导致耗时长
- 使用批处理
- 少量请求,多次插入:请求虽然减少了,但是插入一条数据,仍然使用一条 SQL
- 少量请求,组合插入:将多条数据组合成一条 SQL 语句,推荐使用,需要在
yml 配置文件中加入rewriteBatchedStatements=true来开启
如果数据太多,可以分批次批处理,也就是在 `for 循环` 中批处理,因为一次批处理相当于一次网络请求,一次网络请求承载的数据量是有限的
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 拼接rewriteBatchedStatements=true,批量操作的语句在执行时能够被重写
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username: ……
password: ……// 使用IService批量插入
@Test
public void testIServiceSaveBatch() {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("Jeans", "Japen", 2));
users.add(new User("Franqey", "France", 2));
users.add(new User("Slim Boogie", "America", 1));
userService.saveBatch(users);
}半自动 SQL
[!quote] 半自动 SQL 半自动 SQL 是指 sql 语句的前半部分还是写在 XML 文件里,而
WHERE 条件使用 MyBatis-Plus 来写
- 在开发规范中,sql 语句不能写在业务代码里,所以业务代码里只写 MP 的 WHERE 条件
- MP 不擅长生成 sql 语句的前半部分,只擅长编写 WHERE 条件
- 测试类
// 半自动sql,实现动态SET
@Test
public void testSemiAutoUpdate() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<User>()
.eq(User::getId, 1);
userService.increaseAuthority(lambdaQueryWrapper);
}- Service 接口
public interface UserService extends IService<User> {
void increaseAuthority(LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper);
}- Service 实现类
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
// 将用户权限加1
@Override
public void increaseAuthority(LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper) {
userMapper.incrementAuthority(lambdaQueryWrapper);
}
}- Mapper
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
// 将参数LambdaQueryWrapper命名为ew,方便后续xml引用
void incrementAuthority(@Param("ew") LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper);
}- xml 文件
<!-- ${ew.customSqlSegment} 就是一个WHERE片段 -->
<!-- ew是传入的LambdaQueryWrapper -->
<!-- customSqlSegment是LambdaQueryWrapper里的一个属性,表示拼接的WHERE片段 -->
<update id="incrementAuthority">
UPDATE user
SET user_authority = user_authority + 1 ${ew.customSqlSegment}
</update>高阶用法
代码生成
[!quote] 代码生成
由于各种
IService,BaseMapper的格式比较固定,所以我们可以借助代码生成器来快速生成代码生成的方式:
- 插件
- MyBatisX:功能丰富
- MyBatisPlus:更好地适配 MP
- easycode
- MP 官方的代码生成器配置代码:太复杂
- 右键数据库表,选择 MyBatisX-Generator

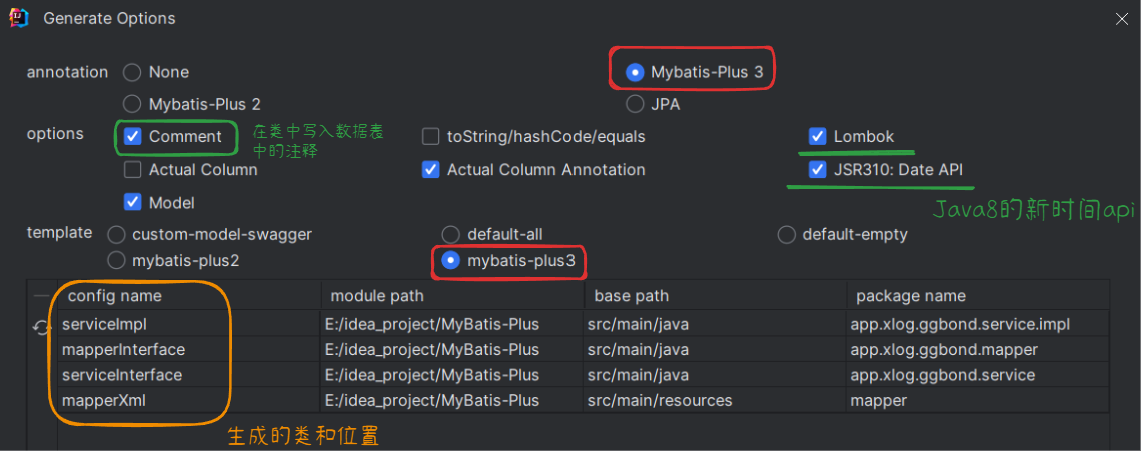
Db Kit
[!quote] Db Kit Db Kit 允许通过静态调用的方式执行 CRUD 操作,从而避免了在 Spring 环境下的 Service 循环注入问题【
比如】UserService需要注入RoleService,而RoleService也需要注入UserService
listObjs(Wrapper, Lambda表达式)可以通过 Lambda 表达式将返回的 Entity 再次加工
// 在role表中通过role_id查询角色名称
QueryWrapper<Role> queryRoleWrapper = new QueryWrapper<Role>()
.setEntityClass(Role.class)
.select("role_name")
.in("role_id", roleIds);
// 本来返回的是 List<Role>,但是通过Role::getRoleName,将返回RoleName类型的集合
List<String> roleNameList = Db.listObjs(queryRoleWrapper, Role::getRoleName);classDiagram
class User {
+Integer UserId
+String UserName
+String UserPassword
+Integer UserAuthority
-List<String> Roles
}
class UserRole {
+Integer UserRoleId
+Integer UserId
+Integer RoleId
}
class Role {
+Integer RoleId
+String RoleName;
+String RoleDescription;
}
UserRole <|-- User :
UserRole <|-- Role :- Service 实现类
// 根据id,查询用户的信息和用户的角色名称,一共涉及三张表:user,user_role,role
@Override
public User getUserAndRoleName(int id) {
// 先去user表中查基础信息
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.eq("user_id", id);
User user = getOne(queryWrapper);
// 此时的user是没有role属性的
// 通过user_role表查询用户对应的角色id
QueryWrapper<UserRole> queryUserRoleWrapper = new QueryWrapper<UserRole>()
.setEntityClass(UserRole.class)
.select("role_id")
.eq("user_id", id);
List<Integer> roleIds = Db.listObjs(queryUserRoleWrapper, UserRole::getRoleId);
// 在role表中通过role_id查询角色名称
QueryWrapper<Role> queryRoleWrapper = new QueryWrapper<Role>()
.setEntityClass(Role.class)
.select("role_name")
.in("role_id", roleIds);
List<String> roleNameList = Db.listObjs(queryRoleWrapper, Role::getRoleName);
user.setRoles(roleNameList);
return user;
}逻辑删除
[!quote] 逻辑删除
逻辑删除 就是这条数据展示给用户时,像是被删除了,但是依旧保留在数据库中【
方便后续溯源】,比如商品的订单信息,用户要删除订单,用户看不见了,但是我们不能真的在数据库中删除,因为这个订单信息还是有用的
- 不推荐使用,因为会影响性能【
因为要每个 SQL 语句都多加一个条件】实现方法:
- 在数据库表中添加一个
delete字段,用于标识这条数据是否被逻辑删除了- 在配置文件中开启逻辑删除
- 不使用 MP 的逻辑删除【
需要自己手动给每个 SQL 语句都多加一个】,非常麻烦WHERE条件
// 表示这条数据没有被逻辑删除
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.eq("user_id", id)
.eq("user_delete", 0);- 使用 MP 开启配置【
不用改动之前的 SQL 语句,MP 会默认在所有 SQL 语句加逻辑删除的 WHERE 条件】
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: 数据库标记逻辑删除的字段名 # 字段类型可以是Integer, Booolean
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)自动映射枚举
为了增强代码的可读性,有时会使用枚举,但是枚举跟数据库表中的字段是不会自动映射的,我们需要手动映射又很麻烦,这时可以使用 MP 提供的自动枚举映射
- 给枚举类的枚举字段添加
@EnumValue,表示数据库字段【存储的是 1,2,3】映射到的是这个属性
@TableName(value = "user")
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
…… 其他字段
/**
* 1 正常, 2 锁定, 3 冻结
*/
@NonNull
@TableField(value = "user_status")
private UserStatus userStatus;
// 枚举用户状态
public enum UserStatus {
NORMAL(1, "正常"),
LOCKED(2, "锁定"),
FROZEN(3, "冻结");
@EnumValue
private final int status;
private final String description;
UserStatus(int status, String description) {
this.status = status;
this.description = description;
}
}
}插件
分页查询
- 添加 MyBatisPlusConfig 配置类,配置分页插件,添加进 MyBatisPlus 拦截器中
package app.xlog.ggbond.config;
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
// 1.创建分页插件,可以使用paginationInnerInterceptor添加各种分页配置
PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor = new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL);
// 2.把分页插件添加进拦截器
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor);
return interceptor;
}
}WARNING
- 如果配置多个插件, 切记分页最后添加
- 如果有多个数据源可以不配具体类型,否则都建议配上具体的 DbType
- 创建 Page 对象,使用 IService 中的 page() 进行分页查询
[!quote] Page 类
属性名 类型 默认值 描述 records List<T> emptyList 这一页 page 的数据 total Long 0 数据库表中的总记录数 size Long 10 每页显示条数,默认 10 current Long 1 当前的页码 orders List<OrderItem> emptyList 排序字段信息 optimizeCountSql boolean true 自动优化 COUNT SQL optimizeJoinOfCountSql boolean true 自动优化 COUNT SQL 是否把 join 查询部分移除 searchCount boolean true 是否进行 count 查询 maxLimit Long 单页分页条数限制 countId String XML 自定义 count 查询的 statementId
// 分页查询
@Test
public void testPageSelect() {
// 1.创建Page对象,传入当前页和每页显示的数量
Page<User> pageOne = new Page<>(1, 2);
Page<User> pageTwo = new Page<>(2, 2);
Page<User> pageThree = new Page<>(3, 2);
userService.page(pageOne);
System.out.println("第一页:" + pageOne.getRecords());
System.out.println("-------------");
userService.page(pageTwo);
System.out.println("第二页" + pageTwo.getRecords());
System.out.println("-------------");
userService.page(pageThree);
System.out.println("第三页" + pageThree.getRecords());
}
---
第一页:[User(userId=1, userName=kite, userPassword=Japen, userAuthority=4, userStatus=NORMAL, roles=null), User(userId=2, userName=nelson, userPassword=France, userAuthority=1, userStatus=NORMAL, roles=null)]
-------------
第二页[User(userId=3, userName=greenteck, userPassword=Canada, userAuthority=2, userStatus=NORMAL, roles=null), User(userId=4, userName=jaygee, userPassword=Korea, userAuthority=2, userStatus=LOCKED, roles=null)]
-------------
第三页[User(userId=5, userName=Hoan, userPassword=Korea, userAuthority=2, userStatus=LOCKED, roles=null), User(userId=7, userName=Jeans, userPassword=Japen, userAuthority=2, userStatus=FROZEN, roles=null)]